Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Explore the top 10 prompt engineering techniques for 2025, including zero-shot, few-shot, and chain-of-thought prompting, to enhance AI interactions.
In the rapidly evolving landscape of artificial intelligence, prompt engineering has emerged as a critical skill for effectively interacting with large language models (LLMs) like GPT-4, Claude, and LLaMA. By crafting precise prompts, users can guide these models to produce desired outputs, making prompt engineering an essential tool for developers, researchers, and AI enthusiasts.
This article delves into the top 10 prompt engineering techniques that are shaping AI interactions in 2025. These methods will help you harness the full potential of LLMs, ensuring accurate and efficient outcomes.
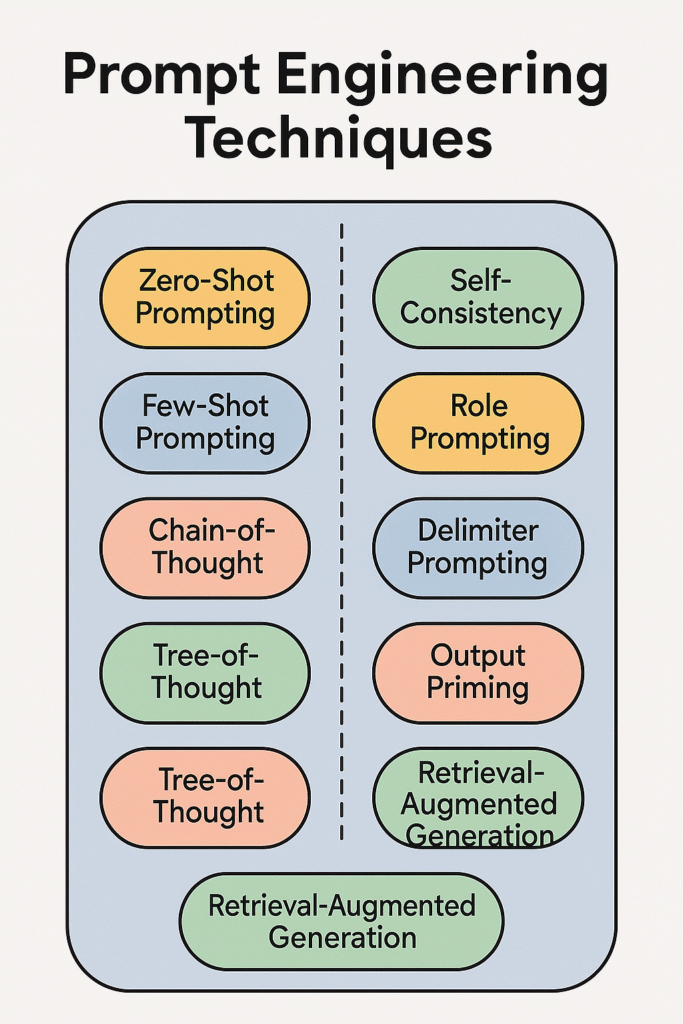
Zero-shot prompting involves providing the model with a task description without any examples. This technique relies on the model’s pre-trained knowledge to generate responses.
Example:
Prompt: “Translate the following English sentence to French: ‘Good morning.'”
Output: “Bonjour.”
Zero-shot prompting is useful for straightforward tasks where the model’s general knowledge suffices.
Few-shot prompting provides the model with a few examples to illustrate the desired task. This helps the model understand the pattern and generate appropriate responses.
Example:
Prompt:
“Translate the following English sentences to French:
Output: “Je vais bien.”
Few-shot prompting is effective for tasks requiring specific formats or styles.
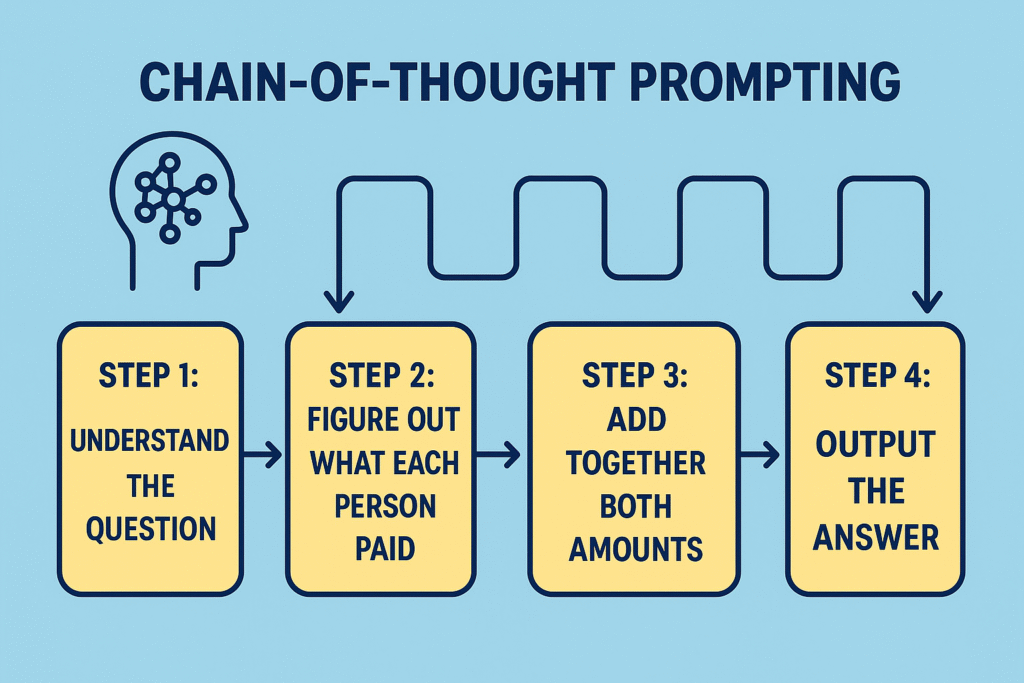
Chain-of-thought (CoT) prompting encourages the model to reason through a problem step-by-step before arriving at an answer. This technique enhances the model’s performance on complex tasks.
Example:
Prompt: “If there are 3 apples and you take away 2, how many do you have? Let’s think step by step.”
Output: “You have 2 apples because you took them.”
CoT prompting is particularly useful for mathematical and logical reasoning tasks.
Self-consistency prompting involves generating multiple reasoning paths and selecting the most consistent answer. This technique improves the reliability of the model’s responses.
Example:
Prompt: “Solve: What is 15 multiplied by 3? Let’s think step by step.”
Output: “15 times 3 is 45.”
By comparing multiple reasoning paths, self-consistency prompting ensures more accurate results.
Tree-of-thought prompting expands on CoT by exploring multiple reasoning paths simultaneously, allowing the model to backtrack and consider alternative solutions. This method is beneficial for tasks requiring exploration of various possibilities.
Example:
Prompt: “Find all possible combinations of coins that sum to 10 cents using 1, 5, and 10 cent coins.”
Output: “1) 10¢; 2) 5¢ + 5¢; 3) 5¢ + 1¢ + 1¢ + 1¢ + 1¢ + 1¢; …”
Tree-of-thought prompting is ideal for combinatorial and exploratory tasks.
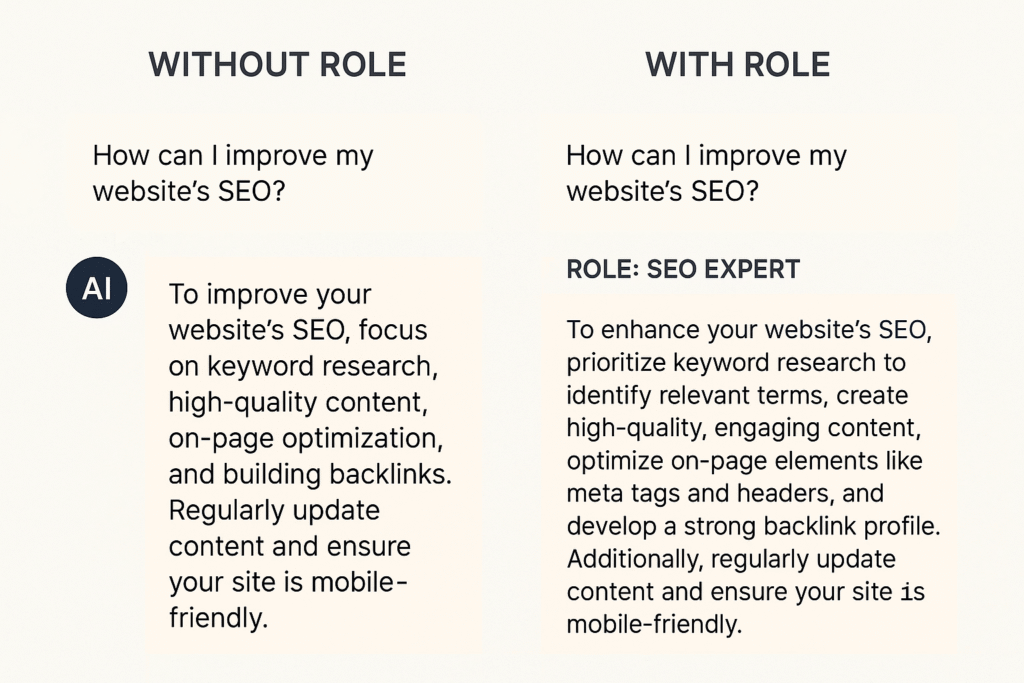
Role prompting assigns a specific role or persona to the model, guiding it to respond in a particular manner. This technique is useful for simulations and role-based interactions.
Example:
Prompt: “You are a helpful assistant. Explain the theory of relativity in simple terms.”
Output: “The theory of relativity, developed by Einstein, explains how time and space are linked for objects moving at a constant speed in a straight line…”
Role prompting helps tailor the model’s responses to specific contexts.
Delimiter prompting uses specific markers to separate different parts of the prompt, providing clarity and structure. This technique enhances the model’s understanding of the task.
Example:
Prompt: “### Instruction: Translate to Spanish.### Input: ‘Good night.'”
Output: “Buenas noches.”
Using delimiters helps in organizing complex prompts effectively.
Output priming involves starting the desired output to guide the model’s response. This technique is useful for ensuring the model follows a specific format.
Example:
Prompt: “Write a haiku about the ocean.
Ocean waves crash
Output: “Ocean waves crash
Against the silent shoreline
Whispers of the deep.
Output priming is effective for creative writing and structured outputs.
RAG combines information retrieval with generation, allowing the model to access external data sources for more accurate and up-to-date responses. This technique is valuable for tasks requiring current information.
Example:
Prompt: “Using the latest data, summarize the current state of the global economy.”
Output: “As of May 2025, the global economy is experiencing…”
RAG enhances the model’s ability to provide informed and relevant answers.
Automatic prompt generation uses one model to create prompts for another, optimizing the interaction process. This technique streamlines prompt creation and ensures consistency.
Example:
Prompt: “Generate a prompt that asks for a summary of a news article.”
Output: “Summarize the key points of the following news article: [Article Text]”
Automatic prompt generation is beneficial for scaling prompt engineering efforts.
Mastering these prompt engineering techniques will empower you to interact more effectively with AI models, unlocking their full potential. As AI continues to evolve, staying updated with these methods will be crucial for developers, researchers, and enthusiasts alike.
Ready to elevate your AI interactions? Start implementing these prompt engineering techniques today and experience the difference in your AI-driven projects.